The Internet of Things (IoT) has provided ways to improve nearly every industry imaginable. In agriculture, IoT has not only provided solutions to often time-consuming and tedious tasks but is totally changing the way we think about agriculture. What exactly is a smart farm, though? Here is a rundown of what smart farming is and how it’s changing agriculture.
What Is a Smart Farm?
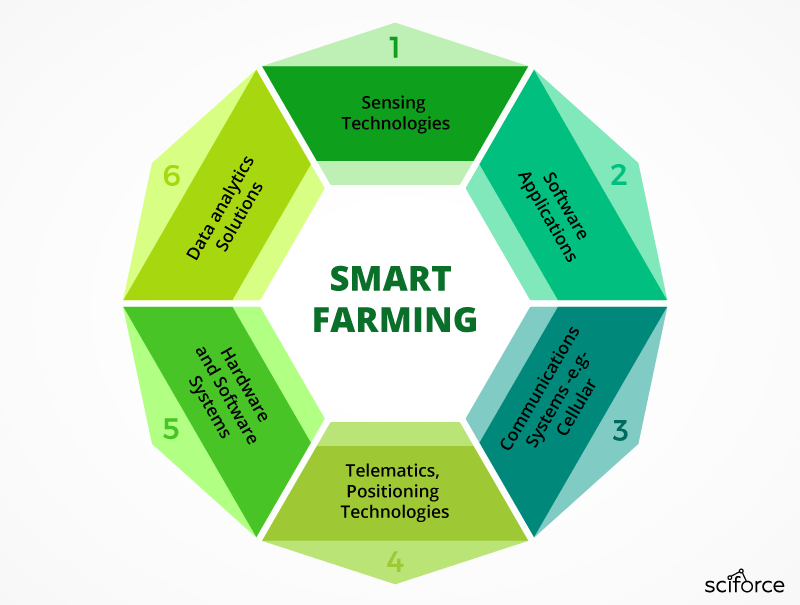
Smart farming refers to managing farms using modern Information and communication technologies to increase the quantity and quality of products while optimizing the human labor required.
Among the technologies available for present-day farmers are:
- Sensors: soil, water, light, humidity, temperature management
- Software: specialized software solutions that target specific farm types or applications agnostic IoT platforms
- Connectivity: cellular, LoRa
- Location: GPS, Satellite
- Robotics: Autonomous tractors, processing facilities
- Data analytics: standalone analytics solutions, data pipelines for downstream solutions
Armed with such tools, farmers can monitor field conditions and make strategic decisions for the whole farm or a single plant without even needing to step foot in the field.
The driving force of smart farming is IoT — connecting machines and sensors integrated on farms to make farming processes data-driven and automated.
The IoT-Based Smart Farming Cycle
The core of IoT is the data you can draw from things and transmit over the internet. To optimize the farming process, IoT devices installed on a farm should collect and process data in a repetitive cycle that enables farmers to react quickly to emerging issues and changes in ambient conditions. Smart farming follows a cycle similar to this one:
1. Observation . Sensors record observational data from the crops, livestock, soil, or atmosphere.
2. Diagnostics. The sensor values are fed to a cloud-hosted IoT platform with predefined decision rules and models—also called “business logic”—that ascertain the condition of the examined object and identify any deficiencies or needs.
3. Decisions . After issues are revealed, the user, and/or machine learning-driven components of the IoT platform determine whether location-specific treatment is necessary and, if so, which.
4. Action . After end-user evaluation and action, the cycle repeats from the beginning.
IoT Solutions to Agricultural Problems
Many believe that IoT can add value to all areas of farming, from growing crops to forestry. While there are several ways that IoT can improve farming, two of the major ways IoT can revolutionize agriculture are precision farming and farming automation.
Precision Farming
Precision farming, or precision agriculture, is an umbrella concept for IoT-based approaches that make farming more controlled and accurate. In simple words, plants and cattle get precisely the treatment they need, determined by machines with superhuman accuracy. The biggest difference from the classical approach is that precision farming allows decisions to be made per square meter or even per plant/animal rather than for a field.
By precisely measuring variations within a field, farmers can boost the effectiveness of pesticides and fertilizers, or use them selectively.
Precision Livestock Farming
As is the case of precision agriculture, smart farming techniques enable farmers better to monitor the needs of individual animals and adjust their nutrition accordingly, thereby preventing disease and enhancing herd health.
Large farm owners can use wireless IoT applications to monitor the location, well-being, and health of their cattle. With this information, they can identify sick animals, so that they can be separated from the
Automation in Smart Greenhouses
Traditional greenhouses control the environmental parameters through manual intervention or a proportional control mechanism, which often results in production loss, energy loss, and increased labor costs.
IoT-driven smart greenhouses can intelligently monitor as well as control the climate, eliminating the need for manual intervention. Various sensors are deployed to measure the environmental parameters according to the specific requirements of the crop. That data is stored in a cloud-based platform for further processing and control with minimal manual intervention.
Agricultural Drones
Agriculture is one of the major verticals to incorporate both ground-based and aerial drones for crop health assessment, irrigation, crop monitoring, crop spraying, planting, soil
Since drones collect multispectral, thermal, and visual imagery while flying, the data they gather provide farmers with insights into a whole array of metrics: plant health indices, plant counting and yield prediction, plant height measurement, canopy cover mapping, field water pond mapping, scouting reports, stockpile measuring, chlorophyll measurement, nitrogen content in wheat, drainage mapping, weed pressure mapping, and so on.
Importantly, IoT-based smart farming doesn’t only target large-scale farming operations; it can add value to emerging trends in agriculture like organic farming, family farming, including breeding particular cattle and/or growing specific cultures, preservation of particular or
Third Green Revolution
Smart farming and IoT-driven agriculture are paving the way for what can be called a Third Green Revolution.
Following the plant breeding and genetics revolutions, the Third Green Revolution is taking over agriculture. That revolution draws upon the combined application of data-driven analytics technologies, such as precision farming equipment, IoT, big data analytics, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs or drones), robotics, etc.
In the future, this smart farming revolution depicts, pesticide and fertilizer use will drop while overall efficiency will rise. IoT technologies will enable better food traceability, which in turn will lead to increased food safety. It will also be beneficial for the environment, through, for example, more efficient use of water, or optimization of treatments and inputs.
Therefore, smart farming has a real potential to deliver a more productive and sustainable form of agricultural production, based on a more precise and resource-efficient approach. New farms will finally realize the eternal dream of mankind. It’ll feed our population, which may explode to 9.8 billion by 2050.
This article was originally published on June 22, 2020 and updated January 25, 2023.
Tweet
Share
Share
359 Shares
- Agriculture
- Automation
- Data Analytics
- Drones
- Farming
- Agriculture
- Automation
- Data Analytics
- Drones
- Farming