If you’re involved in the IoT (Internet of Things) space or have embarked on any journey involving real-time data transfer, you’ve probably come across MQTT – Message Queuing Telemetry Transport. MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe network protocol that transports messages between devices, often known as the backbone for IoT. We are going to introduce the key aspect of MQTT, specifically one that’s crucial for large-scale IoT deployments – MQTT broker clustering.
What is MQTT Broker and Cluster?
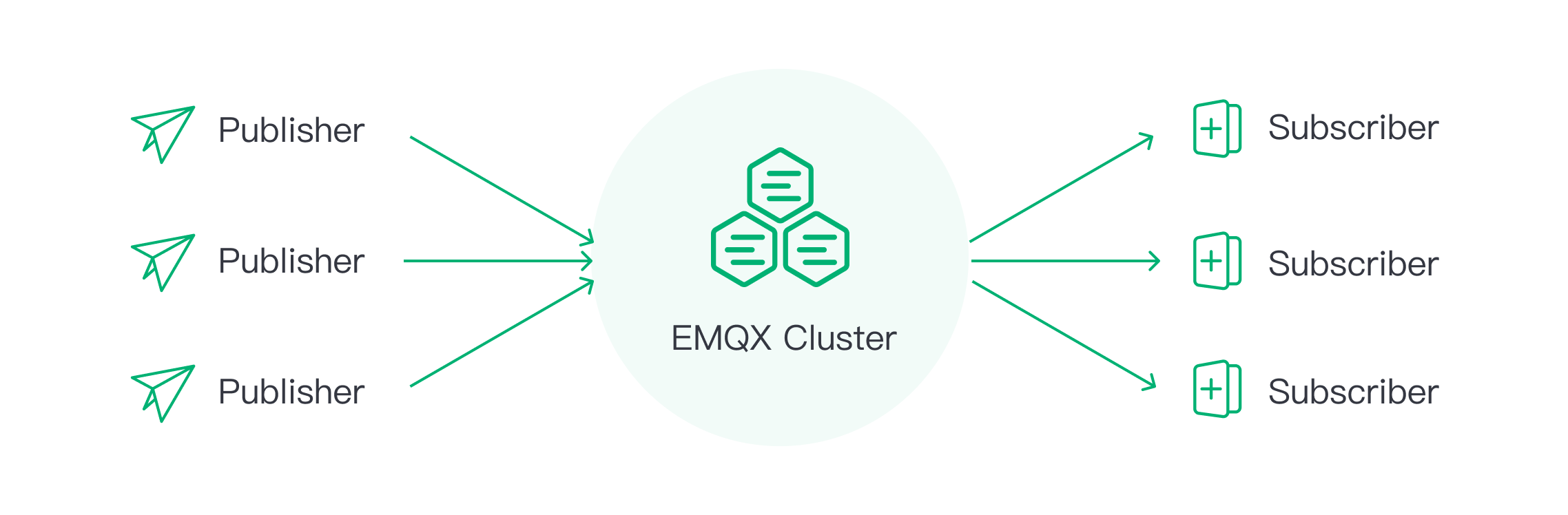
At the heart of MQTT’s publish-subscribe protocol lies the MQTT broker – a central, critical component that handles the transmission of messages between the sender (publisher) and the receiver (subscriber). You may think of the broker as a post office; it accepts messages from various senders, sorts them, and ensures they reach the correct recipients.
In the context of MQTT, publishers send messages (for example, sensor data or commands) to the broker, which then sorts these messages based on topics. Subscribers, which have expressed interest in certain topics, receive these sorted messages from the broker. This mechanism is what allows MQTT to efficiently handle real-time data communication, making it a go-to protocol for IoT applications.
MQTT broker clustering, simply put, is a group of MQTT brokers working together to ensure continuity and high availability. If one broker goes down, others in the cluster are there to pick up the slack, ensuring there’s no disruption in service. Clustering is crucial for businesses and services that cannot afford downtime.
Why MQTT Broker Clustering?
Imagine you have thousands, if not millions, of IoT devices connected to a single MQTT broker, and it crashes or becomes unavailable. All those devices lose their connection, disrupting data flow, and potentially leading to significant losses. By implementing a broker cluster, you spread the load, reduce the risk of such a catastrophe, and ensure scalability for future growth.
At a very high level, below are the benefits of MQTT broker clustering.
- Scalability: One of the key advantages of MQTT broker clustering is its ability to easily scale up to accommodate growth. As the number of connected devices or the volume of data increases in your IoT network, you can add more brokers to the cluster to handle the additional load. This allows your system to expand smoothly and efficiently, without overburdening a single broker or compromising system performance.
- High Availability: High availability is crucial for many IoT applications where constant data flow is essential. In a clustered setup, if one broker goes down, the others in the cluster continue to operate, ensuring uninterrupted service. This redundancy mitigates the risk of a single point of failure, providing a more robust and reliable network for your IoT devices.
- Load Balancing: With the help of DNS resolutions or load-balancers, MQTT broker clusters can be deployed to evenly distribute the load among all brokers in the cluster. This prevents any single broker from becoming a performance bottleneck. By sharing the load, each broker can operate more efficiently, leading to improved overall performance and responsiveness. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios with a high volume of messages or a large number of connected devices.
- Centralized Management: Clustering allows for centralized management of brokers, simplifying administration tasks. Instead of dealing with each broker individually, changes can be made across the cluster from a single point, saving time and reducing the likelihood of errors. This centralized approach also provides a comprehensive view of the system’s performance, aiding in monitoring, debugging, and optimizing the network’s performance.
- Maintenance Flexibility: With a single broker, taking down the system for maintenance can cause service disruption. However, with a cluster, you can perform maintenance or upgrades on individual nodes without disrupting the overall service.
Wrapping Up
Whether you’re looking to understand the basics or seeking to navigate the complexities of MQTT broker clustering, this series promises to be an enlightening journey. Stay tuned as we dive into these fascinating topics, one post at a time.
Tweet
Share
Share
- Connectivity
- Network and Protocols
- Connectivity
- Network and Protocols
