
In 2023, 5G networks are expected to be widely available and adopted worldwide for IoT applications. Consequently, businesses using enterprise cellular IoT connectivity solutions will reap the benefits of 5G’s fast speeds and low latency. This will result in enhanced performance of IoT devices and better customer experiences. The Kaleido Intelligence Survey Report 2023 surveyed 800 enterprise decision-makers to understand the pain points and opportunities in cellular IoT connectivity. We will explore key cellular themes discussed in the survey findings webinar which is available to watch on demand.
“Businesses using enterprise cellular IoT connectivity solutions will reap the benefits of 5G’s fast speeds and low latency.”
#1: Avoid Multiple Operators With Global Roaming
IoT devices with cellular connectivity are frequently deployed across multiple countries. As a result, roaming implementation is necessary, according to 66 percent of enterprises needing multi-country connectivity.
One of the primary concerns of those surveyed was ensuring global coverage, managing costs, and obtaining reliable network operator support. 78 percent of enterprises will seek the involvement of multiple network providers for reliable international coverage. This will result in numerous pricing bands, SKUs (Stock Keeping Units), agreements, and portals, often leading to contractual complexity which is time-consuming.
eSIM
The good news for IoT adopters is that they do not need to understand technical device connectivity. Enterprises will increasingly find ready-to-connect cellular modules, experts, and design houses who can support them in their IoT discovery journey and implementation phase. With eSIM (embedded SIM) technology, enterprise deployments benefit from seamlessly connected IoT devices that are automatically optimized as soon as their fleet is activated anywhere in the world. Consequently, they can start transmitting data to drive value from their application.
#2: Device Management & Hardware Design
Enterprises electing to deploy connected devices in multiple regions in-house will face considerable logistical and technical challenges. Enterprises are demanding a combined offering that integrates device and connectivity management from one player. 82 percent selected hardware design services and 84 percent selected device management for data-transmitting IoT machines as an important value-added service from a cellular IoT connectivity provider.
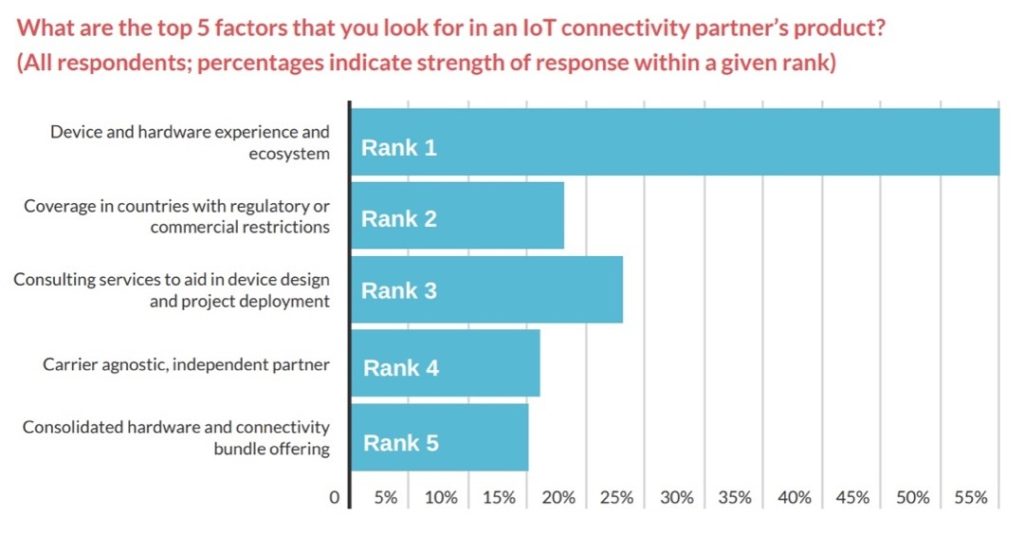
Consolidate IoT Services
The interconnected nature of the hardware, application, and connectivity means enterprises want hardware design and device management services from a single provider. Newcomers want a cost-efficient turnkey solution that supports complex needs with a flexible model for the device’s lifetime. They need a provider who can set up a fleet of IoT devices, provide monitoring services, and improve device functionality. This combined connectivity and hardware offering is available from several module providers such as Quectel and Sierra Wireless.
#3: Vertical-Specific Connectivity Providers
The ability to meet specialized sector-specific use cases through technical and commercial flexibility ranks second in priority for cellular IoT adopters regarding connectivity service providers. 54 percent of cellular IoT adopters mentioned that choosing a connectivity provider with vertical-specific solutions is one of the main non-technical influences in selecting cellular M2M connectivity.
Managed IoT Connectivity Providers
One of the most critical aspects for new adopters is customer support, especially when things go wrong or when initially deploying devices for testing. New cellular IoT adopters will benefit from a vertical-specific network design for their sector and use case. A vertical model’s advantage is minimizing technical faults with compatibility between IoT devices, cloud integration services, and applications.
Cellular IoT newcomers should leverage the expertise of a provider who understands their selected industry. Vertical-specific managed IoT connectivity providers will work with various mobile carriers worldwide to deliver reliable, continuous coverage. The goal is to embark on a partnership with a provider who will execute their IoT strategies and enable their vision.
#4: Advantages of eSIM for Cellular IoT
In the survey, 36 percent of cellular IoT adopters reported using eSIM as part of their IoT connectivity deployment. The main reason was to mitigate risks associated with being locked in with a single operator, mentioned by 66 percent of eSIM users. 59 percent chose eSIM because it offers a reduction in the stock-keeping count.
eSIM excels in multiple aspects as a global IoT GSMA-accredited solution. It offers a dynamic ecosystem that incorporates the ability to dynamically switch to the operator network with the best coverage in a specific region. Customers have the choice of flexibility with eSIM which allows for the operator profiles to be preloaded to ensure that your devices will operate anywhere in the world.
Maximizing Connectivity
More appropriate profiles offering better, more price-competitive coverage in a deployment region can be added remotely with a GSMA-accredited RSP platform. This avoids unnecessary cellular network costs while providing organizations with simplified, functionality-rich, secure connectivity.
Complementing eSIM technology with multi-IMSI can maximize interoperability. The combination of eSIM and multi-IMSI can enable international IoT deployments by leveraging a unified interface that caters to multiple connectivity requirements. In addition, it resolves the permanent roaming issue for specific countries like Turkey and Brazil, where a local profile is required.

#5: eSIM IoT RSP
The significant draw of eSIM IoT RSP is that it will allow eSIM profiles to be downloaded to IoT devices without the complexity and cost of operator integration. The upshot with the SGP 32 specification is that it enables an almost immediate digital subscriber connection speeding up the go-to-market time scale while opening up new opportunities in unreachable markets.
Reassess Connectivity Needs
In addition, enterprises will benefit from zero-touch provisioning, the method of setting up network devices automatically without someone needing to configure it locally. This approach allows for remote and secure dynamic programming of a device in the field based on criteria set at the device level. The new IoT RSP SGP.32 specification significantly helps to increase profile availability, interoperability, and security, making managing eSIM devices across different networks easier.
With IoT’s increasing significance becoming more critical to the bottom line, enterprises must reassess their connectivity needs, highlighted by these cellular themes. Consequently, enterprises should make nuanced decisions when considering global coverage, intelligent-switching capabilities, service delivery, pricing, and IoT data security.
Tweet
Share
Share
- 5G
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- eSIM
- 5G
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- eSIM
