
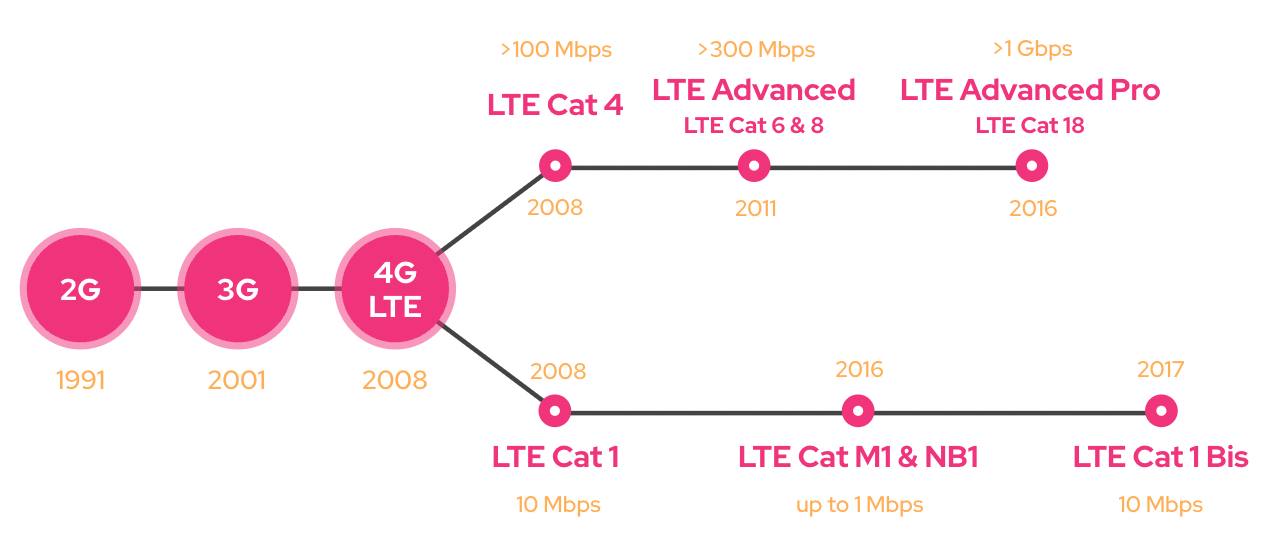
Right now, there are over 20 different LTE categories. From the initial LTE specifications released in 2008 to novel categories classified as LTE Advanced which supports data rates of over 300 Mbps. Also, LTE Advanced Pro with speeds of over 1 Gbps, and LTE for Machines designed for battery-powered, IoT devices. When talking about cellular IoT, people often refer to LTE Cat-M1 (LTE-M), LTE Cat NB1 (NB-IoT), and LTE Cat 1. These technologies support long-range, low-power, and low-cost data transfer, which is ideal for machine-type communication. Cellular IoT is used for building applications which are often comprised of tens of thousands of devices, and applications include warehouse management, smart street lighting, asset tracking, and micro-mobility.
Let’s take a look at the real-world performance metrics of LTE Cat-M1 and LTE Cat 1, allowing you to make a better decision on which technology to use in your application. Let’s put the speed of cellular IoT to the test.
'Cellular IoT is used for building applications which are often comprised of tens of thousands of devices, and applications include warehouse management, smart street lighting, asset tracking, and micro-mobility.' -MonogotoClick To TweetTwo LTE Categories
#1: LTE Cat-M1
LTE Cat-M1 is an LTE standard released in 2016. Designed as a low-power, low-cost wireless technology, it is ideal for battery-powered IoT devices. The tradeoff for using this power-efficient LTE category is the limitation in speed and latency. Most modules support up to 375 kbps uplink (UL) and 300 kbps downlink (DL), and others managed to get their module to send data up to 1 Mbps UL and 500 kbps DL using 1.4 MHz bandwidth. The low-power capabilities of this category make LTE Cat-M1 ideal for IoT devices that need to run on batteries for multiple years.
#2: LTE Cat 1
LTE Cat 1 is one of the oldest LTE categories, released in 2008 supporting 10 Mbps uplink (UL) and 5 Mbps downlink (DL) speed using 5 MHz of bandwidth. This technology has better capabilities in terms of speed and latency, though it requires more power compared to LTE Cat-M1. In comparison to LTE Cat 4, the modules are significantly cheaper and consume less power, thus making LTE Cat 1 more suitable for IoT applications. This LTE standard has been out there for 14 years, and it is one of the most widely available LTE categories globally, ideal for IoT devices that require global connectivity.
In the 3GPP Release 14 which was published in 2017, a variation on LTE Cat 1 was released called LTE Cat 1 Bis. Instead of two integrated antennas, only one antenna is used. This reduces the BOM of the module without compromising on data speeds. However, it disables the device from sending and receiving data at the same time.
Cellular IoT Speed Test
To define the true speed of the different cellular categories, the SIMCom A7676E (LTE Cat 1) and SIM7000E (LTE Cat-M1) modules were connected to a Raspberry Pi over USB. All connectivity interfaces other than the cellular one were disabled and several speed tests were conducted using speedtest.net.
LTE Cat-M1 (SIM7000E)
Results:
| Test | Downlink | Uplink | Latency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.19 Mbps | 0.37 Mbps | 98 ms |
| 2 | 0.25 Mbps | 0.33 Mbps | 100 ms |
| 3 | 0.26 Mbps | 0.32 Mbps | 147 ms |
| 4 | 0.26 Mbps | 0.33 Mbps | 103 ms |
| 5 | 0.25 Mbps | 0.34 Mbps | 137 ms |
| Average | 0.24 Mbps | 0.34 Mbps | 117 ms |
LTE Cat 1 (A7672E)
Results:
| Test | Downlink | Uplink | Latency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.92 Mbps | 4.57 Mbps | 73 ms |
| 2 | 8.71 Mbps | 4.59 Mbps | 67 ms |
| 3 | 9.02 Mbps | 4.73 Mbps | 68 ms |
| 4 | 8.02 Mbps | 4.67 Mbps | 66 ms |
| 5 | 8.90 Mbps | 4.64 Mbps | 72 ms |
| Average | 8.71 Mbps | 4.64 Mbps | 69 ms |
Theoretical vs. Practical Speeds
Looking at the cellular IoT speed test results, it meets the data speed defined in the data sheets quite well. The uplinks are almost identical to the specifications, and the downlinks are somewhat slower. The latency of both technologies is different. The roundtrip time of a data packet is almost 50 ms faster using LTE Cat 1 compared to LTE Cat-M1. The results are an indication of good network quality. With poor network quality, the results will look very different due to a mechanism referred to as adaptive modulation.
Adaptive Modulation
Poor network reception can be the result of different factors. When the distance between the sender and receiver increases, the weaker the radio signal becomes. This makes it harder for the receiver to process the signal. When devices are close to the cell tower, they can still suffer from poor network quality due to obstruction of buildings or objects, or interference (also referred to as noise). When too many radio signals are sent, radio waves start interfering with one another, making it harder for the receiver to filter out the right message.
When sending data wirelessly, bits are translated into radio waves. Each radio wave (referred to as a symbol) can encode a specific amount of information. With good network quality, more bits are encoded in each symbol compared to scenarios with the poor network quality. This is because poor network quality makes it difficult for the receiver to decode radio signals. In practice, this means that cellular devices automatically adjust their data speed. LTE Cat-M1 can send either 2 or 4 bits of data per symbol. LTE Cat 1 can encode 2, 4, or 6 bits per symbol. With 2 bits, you can count to 4 (00, 01, 10, 11), with 4 bits you can count to 16, with 6 bits you can count to 64. This smart mechanism allows cellular devices to automatically improve performance in relation to network quality.
Tweet
Share
Share
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- Mobile
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- IoT Business Strategy
- Mobile
